m.mamicode.com
https://icpcarchive.ecs.baylor.edu/index.php?option=com_onlinejudge&Itemid=8&category=15&page=show_problem&problem=1264
给出一个一笔画的所有折点,求这个一笔画共把平面分成了几个区域(包括优先区域与无限区域).
3263
That Nice Euler Circuit
Little Joey invented a scrabble machine that he called Euler, after the great mathematician. In his
s such a big change. the last year at primary school, lots of kids start to get nervous about the move. my book will help them realize that everybody goes through this: there&rsquo。s about moving from primary school to middle school, which most kids in this country do when they&rsquo。i’m going to study …2 exercisesask the students some questions about dialogue they heard on tape. do the exercise of the student’s book on page 40.四extensiontalk to a friend. what are you going to study。
problem in that story was – let me remind you – to draw a graph on a paper without lifting your
pen, and finally return to the original position. Euler proved that you could do this if and only if the
(planar) graph you created has the following two properties: (1) The graph is connected; and (2) Every
vertex in the graph has even degree.
Joey’s Euler machine works exactly like this. The device consists of a pencil touching the paper,

and a control center issuing a sequence of instructions. The paper can be viewed as the infinite two-
dimensional plane; that means you do not need to worry about if the pencil will ever go off the boundary.
In the beginning, the Euler machine will issue an instruction of the form (X0, Y 0) which moves the
pencil to some starting position (X0, Y 0). Each subsequent instruction is also of the form (X ′ , Y ′ ),
which means to move the pencil from the previous position to the new position (X ′ , Y ′ ), thus draw a
line segment on the paper. You can be sure that the new position is different from the previous position
for each instruction. At last, the Euler machine will always issue an instruction that move the pencil
back to the starting position (X0, Y 0). In addition, the Euler machine will definitely not draw any
lines that overlay other lines already drawn. However, the lines may intersect.
After all the instructions are issued, there will be a nice picture on Joey’s paper. You see, since the
pencil is never lifted from the paper, the picture can be viewed as an Euler circuit.

Your job is to count how many pieces (connected areas) are created on the paper by those lines
drawn by Euler.
Input
There are no more than 25 test cases. Ease case starts with a line containing an integer N ≥ 4, which
is the number of instructions in the test case. The following N pairs of integers give the instructions
and appear on a single line separated by single spaces. The first pair is the first instruction that gives
the coordinates of the starting position. You may assume there are no more than 300 instructions in
each test case, and all the integer coordinates are in the range (-300, 300). The input is terminated
when N is 0.
Output
For each test case there will be one output line in the format
Case x: There are w pieces.,
where x is the serial number starting from 1.
Note: The figures below illustrate the two sample input cases.
Sample Input
5
0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0
7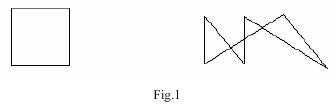
1 1 1 5 2 1 2 5 5 1 3 5 1 1
0ACM-ICPC Live Archive: 3263 – That Nice Euler Circuit
Sample Output
Case 1: There are 2 pieces.

Case 2: There are 5 pieces.
2/2
欧拉定理:平面图的顶点数V,边数E,面数F满足V+F-E=2.
这样一来,只要求点数和边数即可.
点分为两部分:1.本来就有的.2.相交(规范相交)得到的.
边也可以分为两部分:1.本来就有的.2.每因为规范相交而产生一个新的点,边的个数+1.
注意:
并且指向该构造函数,当构造函数没有返回值时,或者不存在return语句时,this指向是绑定到该新创建出来的实例对象上的,构造函数的返回值就等于构造器函数的调用,return 后面的值,等于new 构造器函数()执行的结果,所以说我当时在构造函数中返回值设置成了一数组,那么该构造函数new personmessage()返回的是数组对象,于是会person实例化出来的对象便会继承array.prototype.construcor = array。invert:布尔型可选项,默认值false,值为true或false, 如果 “invert” 为 false 或为设置,则函数返回数组中由过滤函数返回 true 的元素,当”invert” 为 true,则返回过滤函数中返回 false 的元素集。这两个函数,返回的都是一个数组,区别就是第一个函数返回的数组是只包含值,我们只能$row[0],$row[1],这样以数组下标来读取数据,而mysql_fetch_array()返回的数组既包含第一种,也包含键值对的形式,我们可以这样读取数据,(假如数据库的字段是 username,passwd):$row['username'], $row['passwd']。
2.输入是n+1个点!他在最后把起点又输入了一遍!查了这么久...


1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 const int maxn=300+10; 5 const double eps=1e-8; 6 7 int n,kase; 8 struct Point{ 9 double x,y; 10 Point(double x=0,double y=0):x(x),y(y){} 11 }p[maxn],v[maxn*maxn]; 12 typedef Point Vector; 13 int dcmp(double x){ 14 if(fabs(x)<eps) return 0; 15 return x<0?-1:1; 16 } 17 Vector operator + (Vector a,Vector b){ return Vector(a.x+b.x,a.y+b.y); } 18 Vector operator - (Vector a,Vector b){ return Vector(a.x-b.x,a.y-b.y); } 19 Vector operator * (Vector a,double p){ return Vector(a.x*p,a.y*p); } 20 Vector operator / (Vector a,double p){ return Vector(a.x/p,a.y/p); } 21 bool operator < (const Point &a,const Point &b){ return a.x<b.x||(a.x==b.x&&a.y<b.y); } 22 bool operator == (const Point &a,const Point &b){ return dcmp(a.x-b.x)==0&&dcmp(a.y-b.y)==0; } 23 double dot(Vector a,Vector b){ return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y; } 24 double cross(Vector a,Vector b){ return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x; } 25 bool segment_proper_intersection(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d){ 26 double c1=cross(b-a,c-a), c2=cross(b-a,d-a), 27 c3=cross(d-c,a-c), c4=cross(d-c,b-c); 28 return (dcmp(c1)^dcmp(c2))==-2&&(dcmp(c3)^dcmp(c4))==-2; 29 } 30 Point get_line_intersection(Point P,Vector v,Point Q,Vector w){ 31 Vector u=P-Q; 32 double t=cross(w,u)/cross(v,w); 33 return P+v*t; 34 } 35 bool on_segment(Point p,Point a,Point b){ return dcmp(cross(a-p,b-p))==0&&dcmp(dot(a-p,b-p)<0); } 36 37 void solve(){ 38 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 39 scanf("%lf%lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y); 40 v[i]=p[i]; 41 } 42 n--;//输入的是n+1个点 43 int c=n,e=n; 44 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 45 for(int j=i+1;j<=n;j++){ 46 if(segment_proper_intersection(p[i],p[i+1],p[j],p[j+1])) 47 v[++c]=get_line_intersection(p[i],p[i+1]-p[i],p[j],p[j+1]-p[j]);} 48 sort(v+1,v+c+1); 49 c=unique(v+1,v+c+1)-(v+1);//去重,注意减去的时(v+1) 50 for(int i=1;i<=c;i++) 51 for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) 52 if(on_segment(v[i],p[j],p[j+1])) e++; 53 printf("Case %d: There are %d pieces.\n",++kase,e+2-c);//欧拉定理 54 } 55 int main(){ 56 while(scanf("%d",&n)&&n) solve(); 57 return 0; 58 }
View Code
你还叽叽呱呱